1. Application in maintenance scenarios
1. Emergency plugging and fault isolation
Scenario: When the valve core is damaged or the seal fails, remove the faulty valve core, seal the valve hole with a plug, and quickly restore the system operation.
Case:
The proportional valve coil of the injection molding machine is burned → temporarily replaced with a plug to ensure normal pressure supply of other oil circuits.
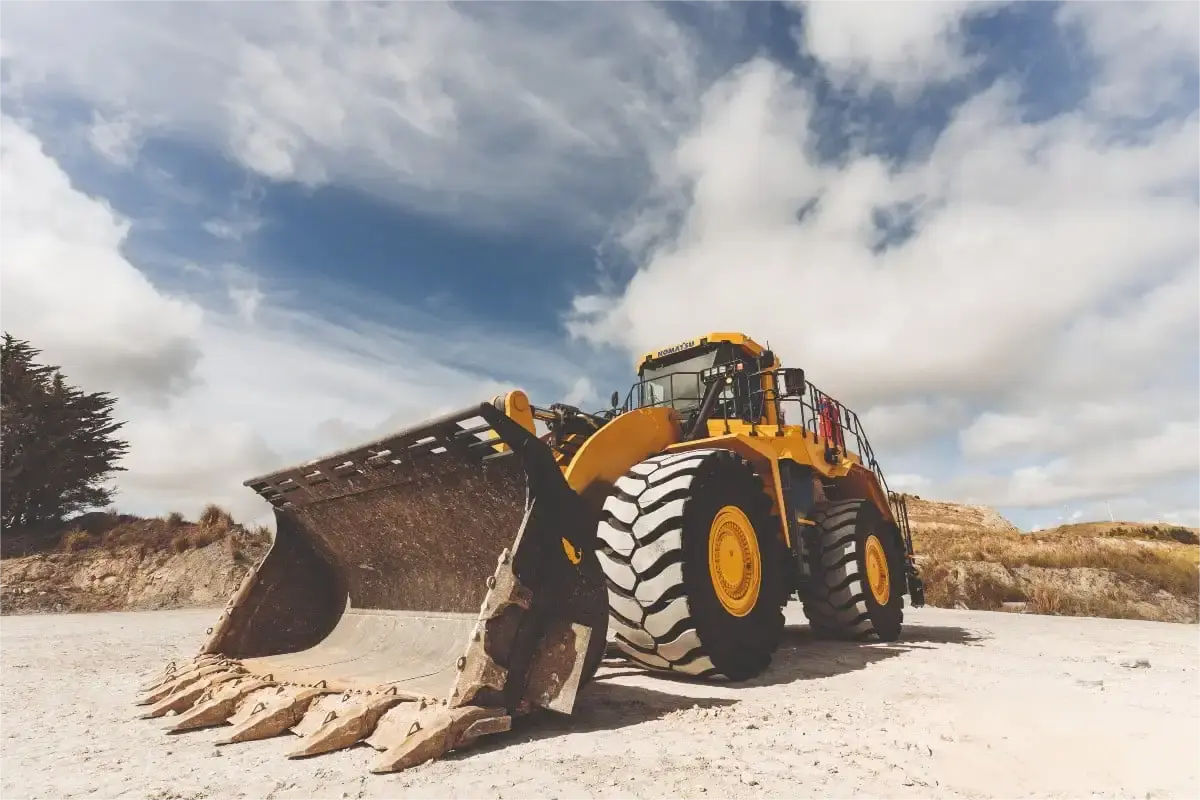
Internal leakage of the multi-way valve plate of the excavator → block the corresponding valve hole and isolate the faulty chamber.
Technical points:
Preferably use O-ring sealing plugs (easy to install and replace within 5 minutes).
When the pressure is greater than 25MPa, a metal cone sealing plug is required (to avoid high-pressure breakdown).
2. Temporary closure of test points
Scenario: After the pressure test is completed after maintenance, the test valve hole is closed.
Operation specification:
Use an external hexagonal pressure test plug (such as HydraForce, SUN series), and no special tools are required for disassembly and assembly.
Apply anti-seizure agent (such as LOCTITE 577) to the threads to prevent thread wear after repeated disassembly and assembly.
2. Application in modification scenarios
1. Reduction of oil circuit functions
Scenario: Simplify the system and close redundant oil circuits.
Case:
The machine tool hydraulic station cancels the workstation fixture function → Use a plug to close the reversing valve hole that controls the fixture.
Engineering machinery removes auxiliary devices (such as hydraulic hammers) → Block the corresponding valve block inlet and outlet oil ports.
Design points:
The plug depth must be ≥1.5 times the thread diameter (to prevent high-pressure oil from shearing the thread).
2. Function upgrade reservation
Scenario: Reserve valve holes for future expansion and temporarily seal them with plugs.
Case:
The press valve block reserves a proportional valve installation position → Pre-install the plug and mark the expansion number (such as "FUTURE V2").